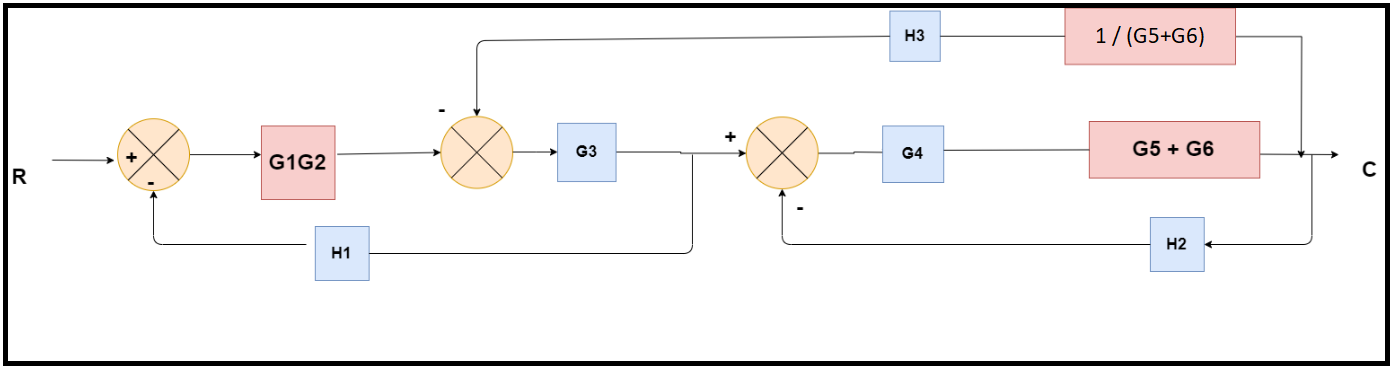
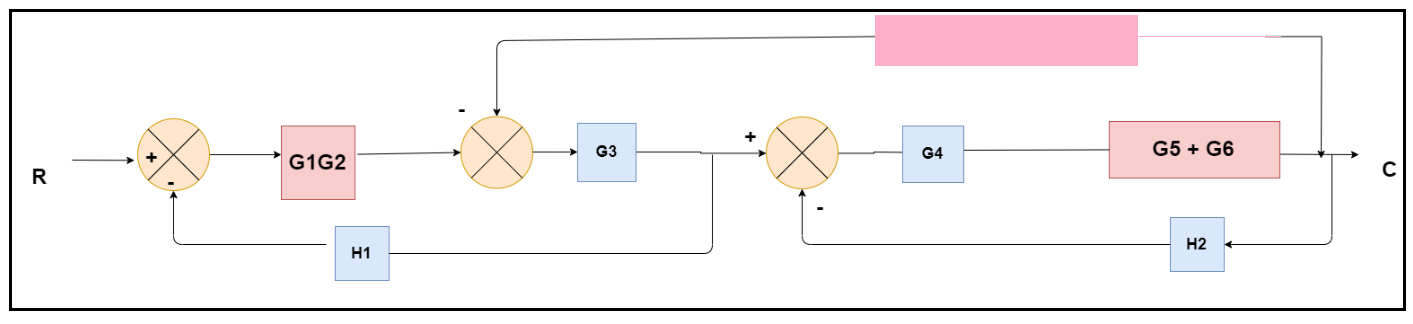
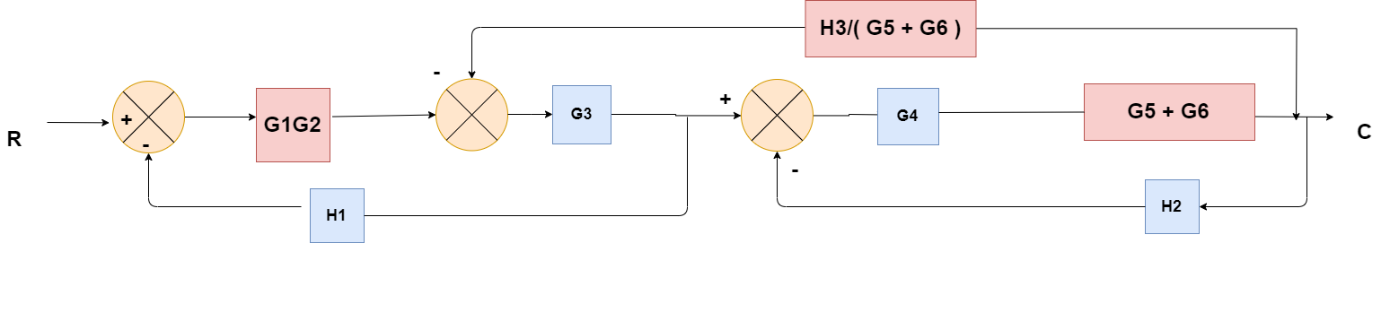
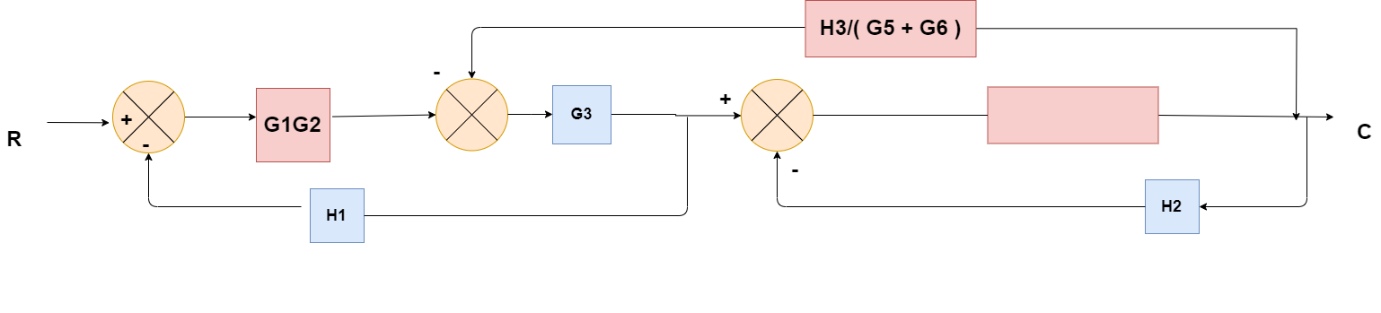
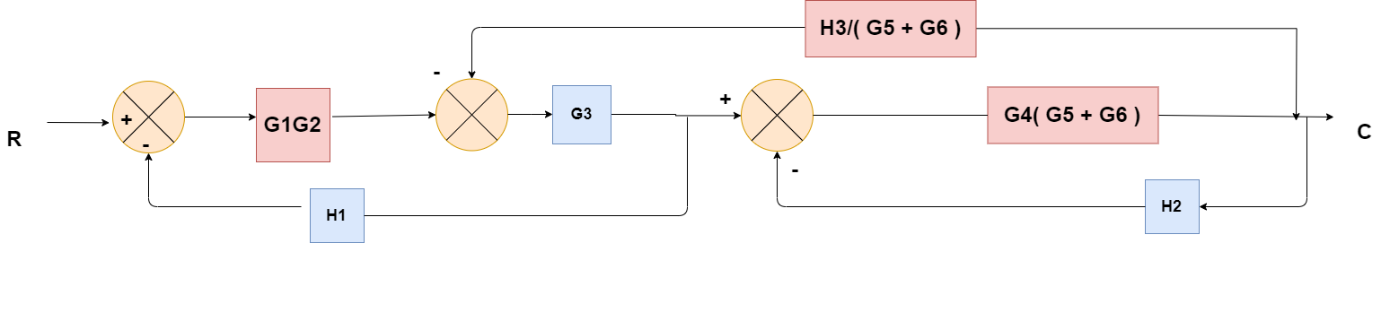
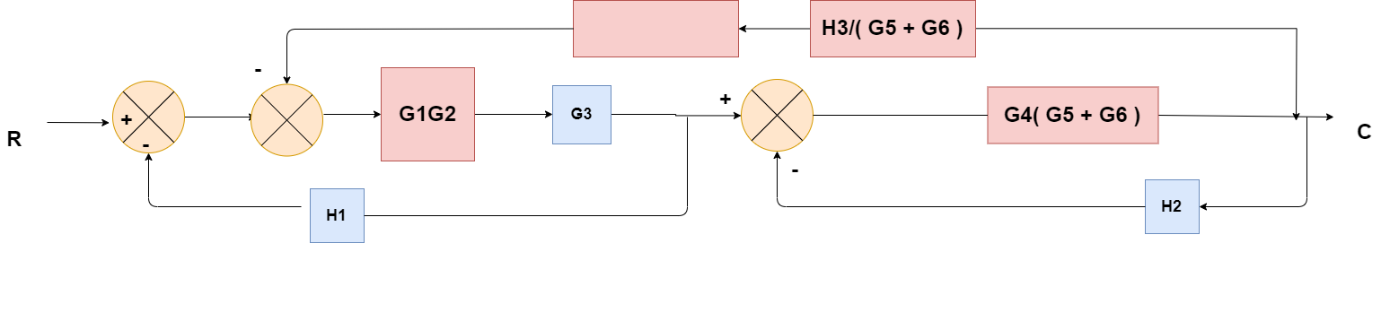
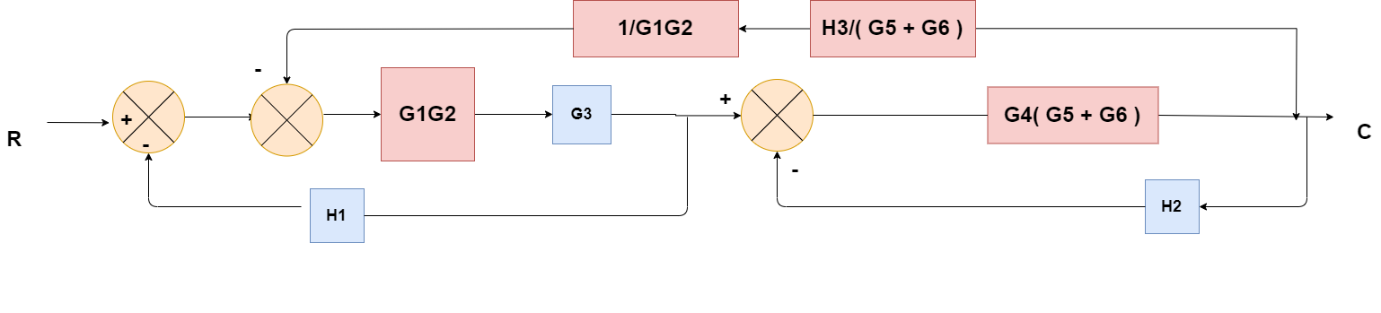
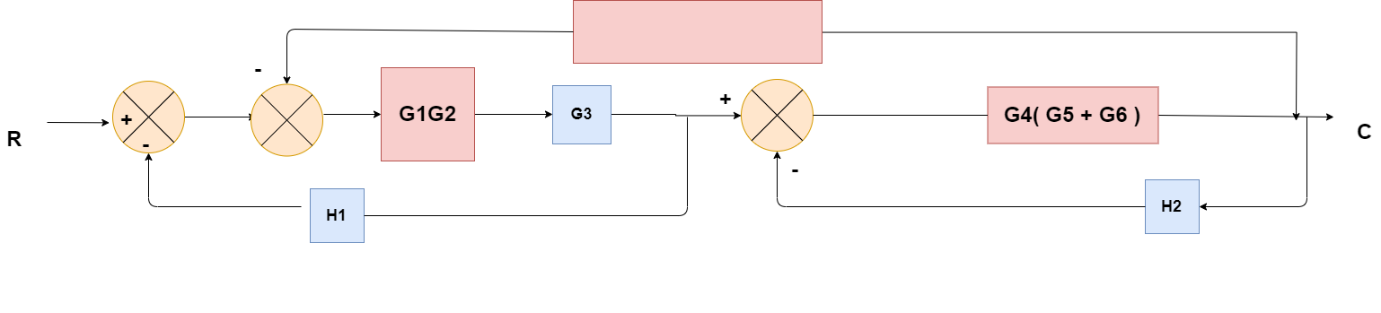
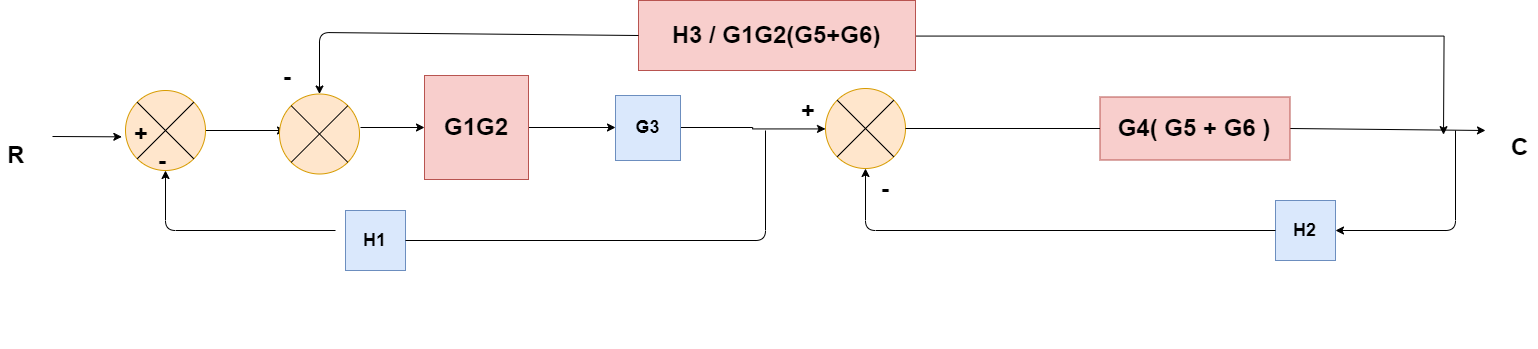
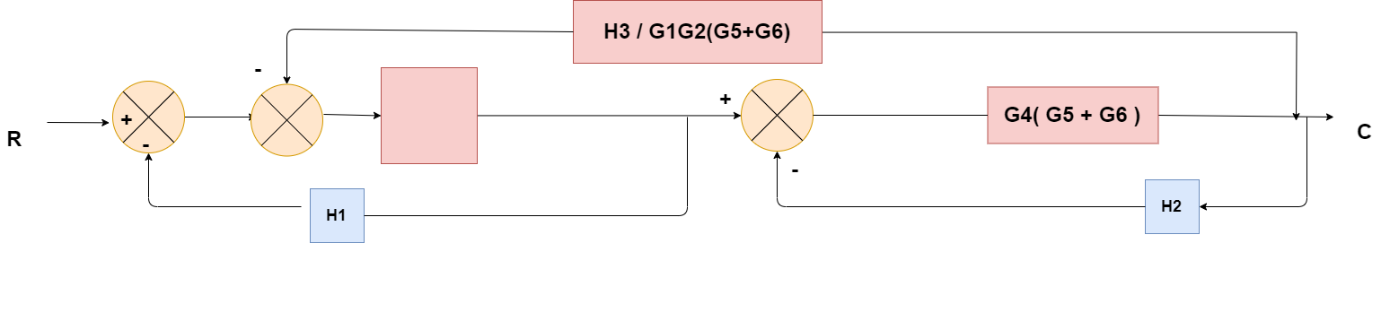
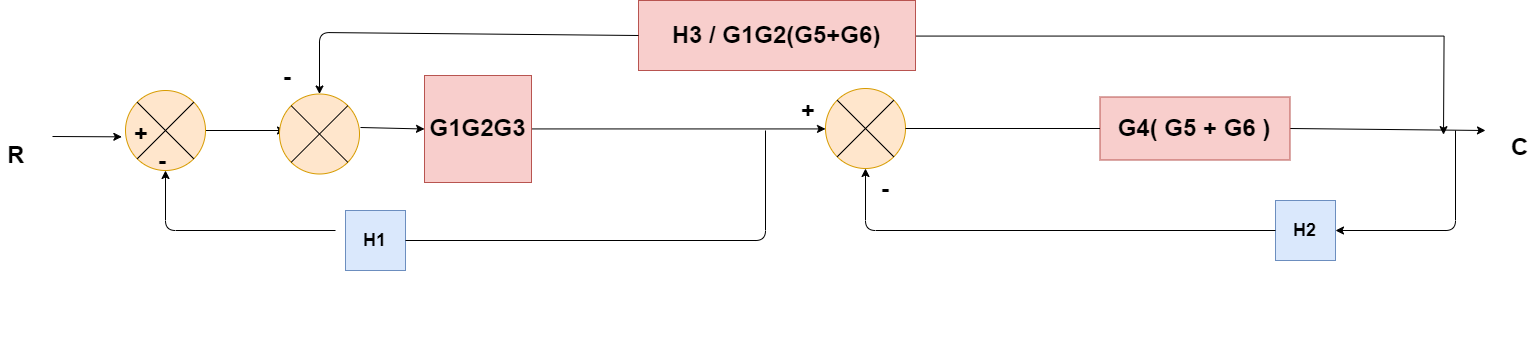
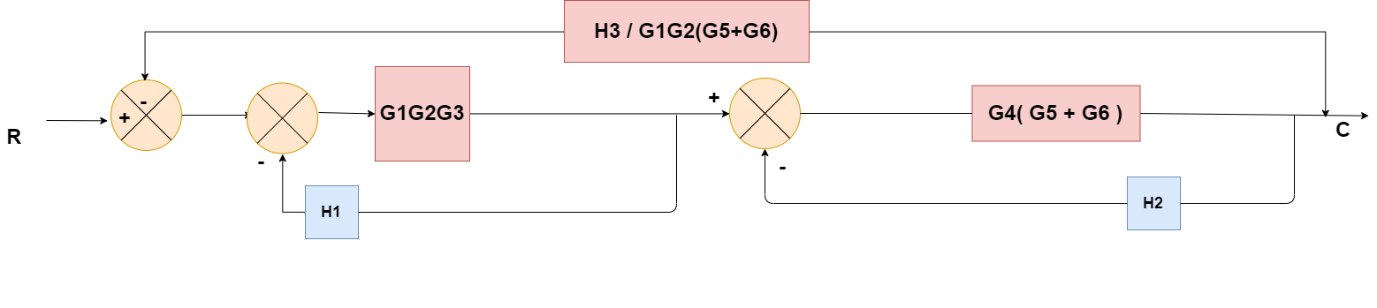
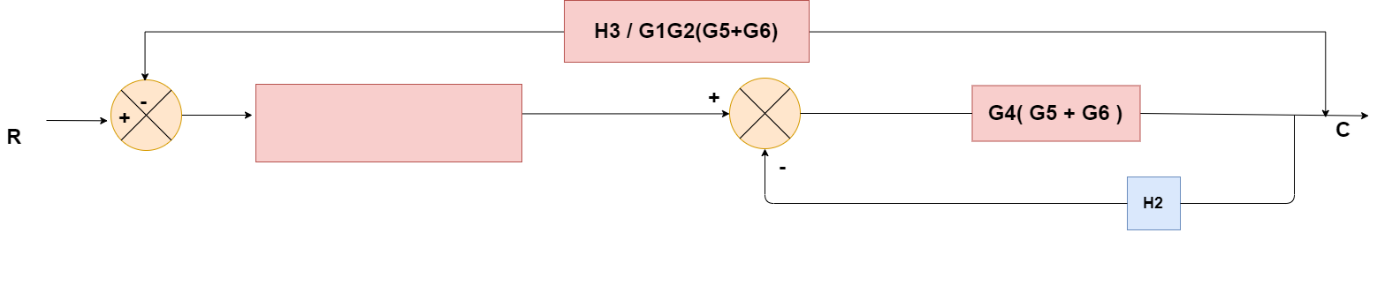
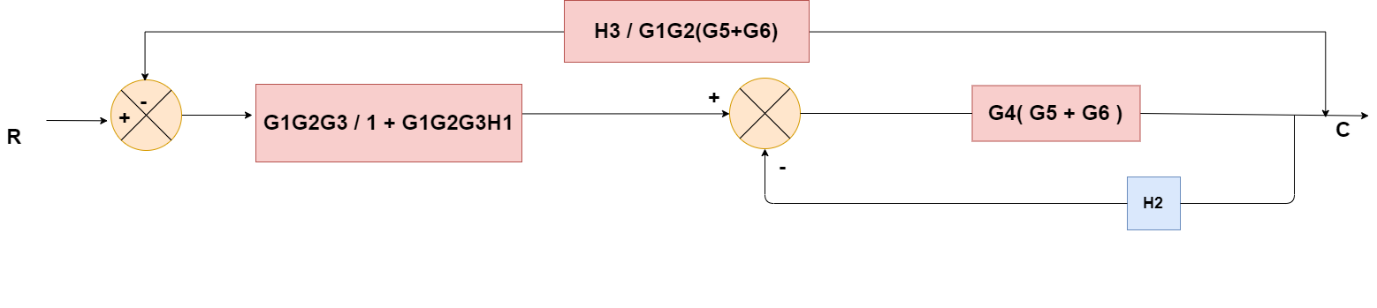
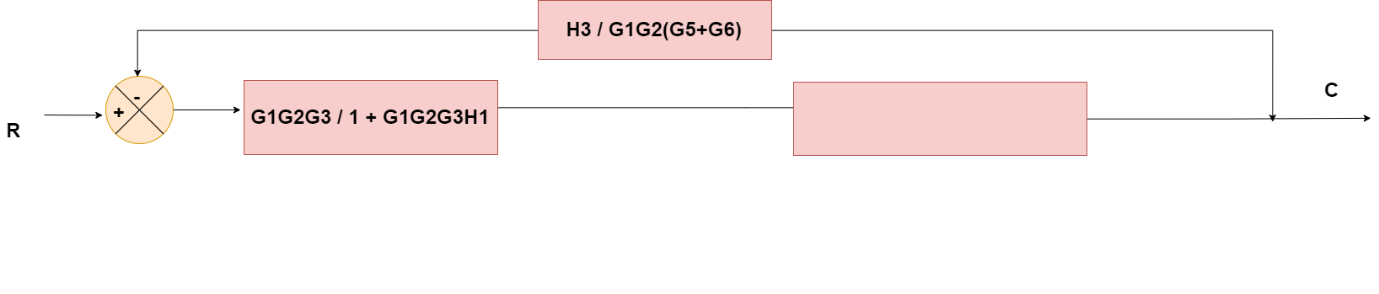
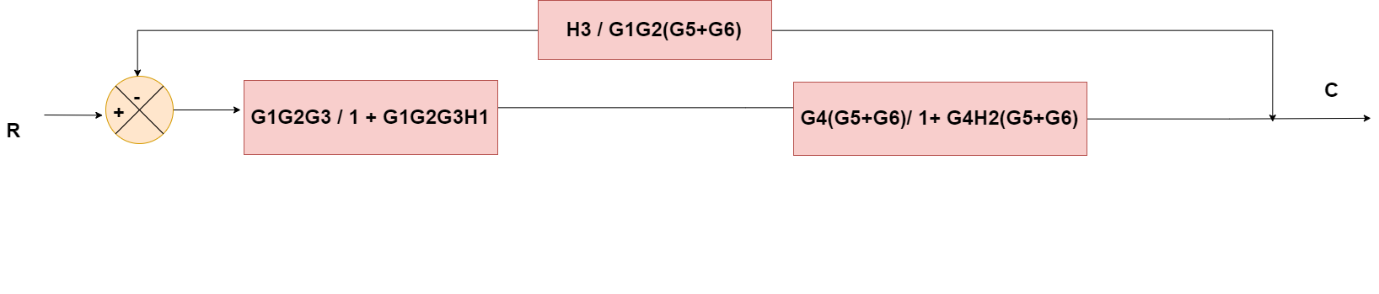
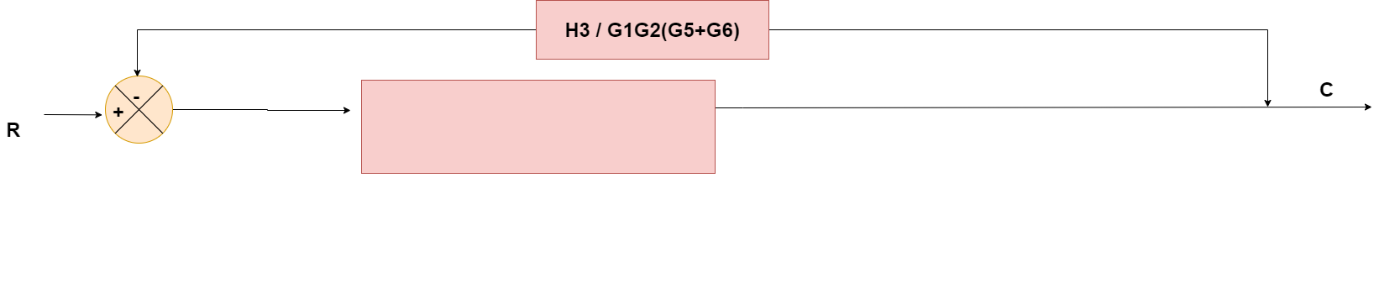
Obtaining Transfer Function using Block Diagram Reduction Technique

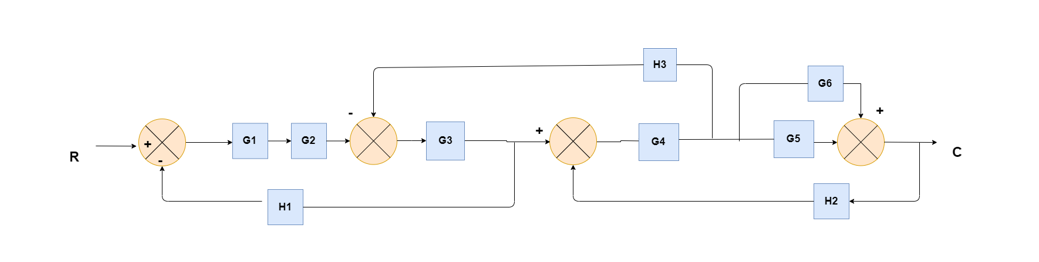
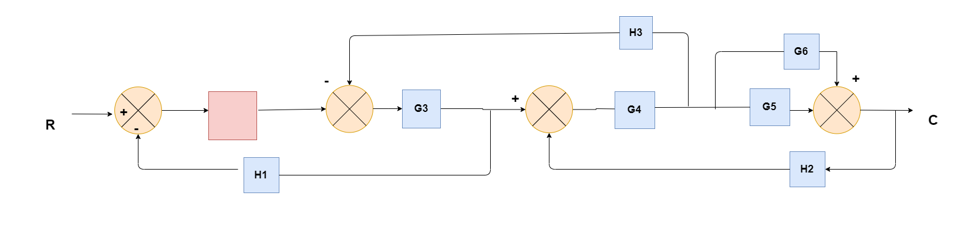
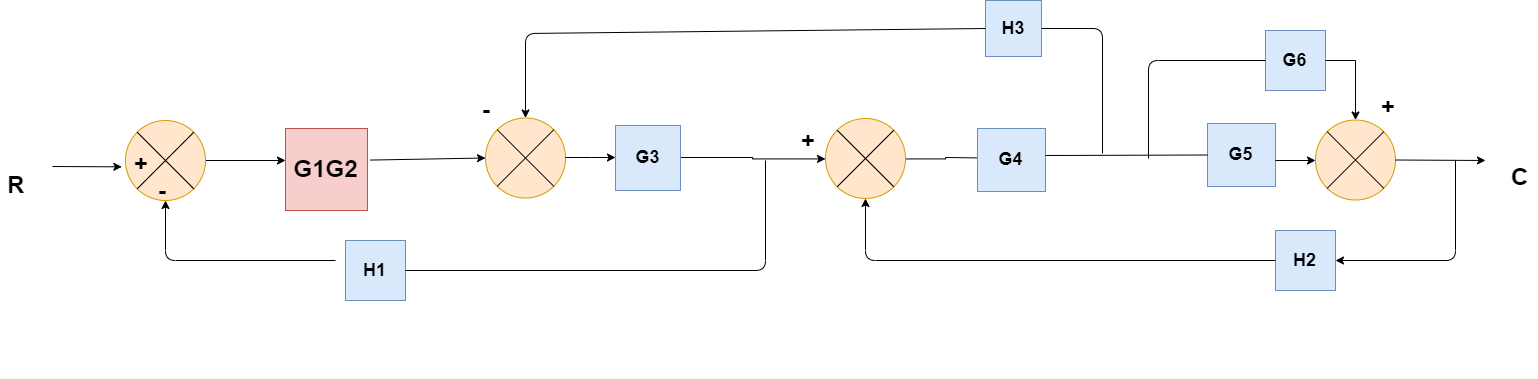
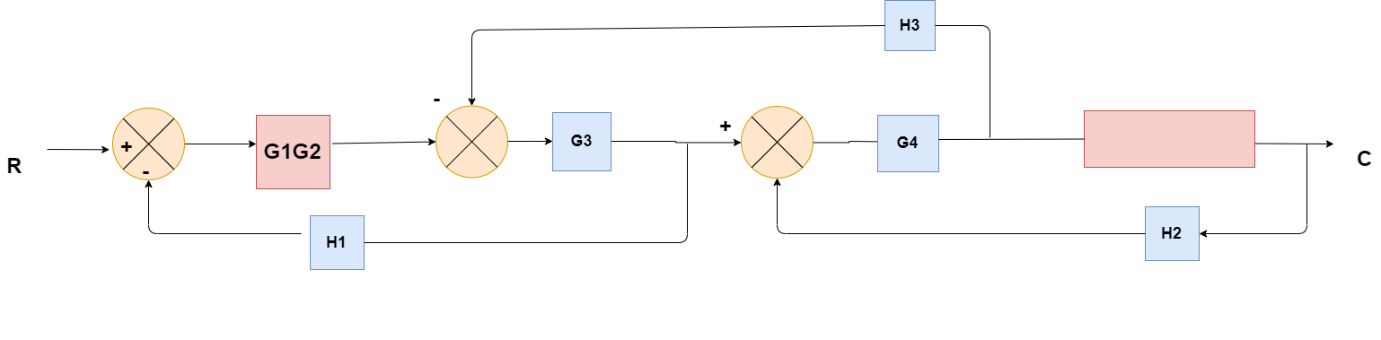
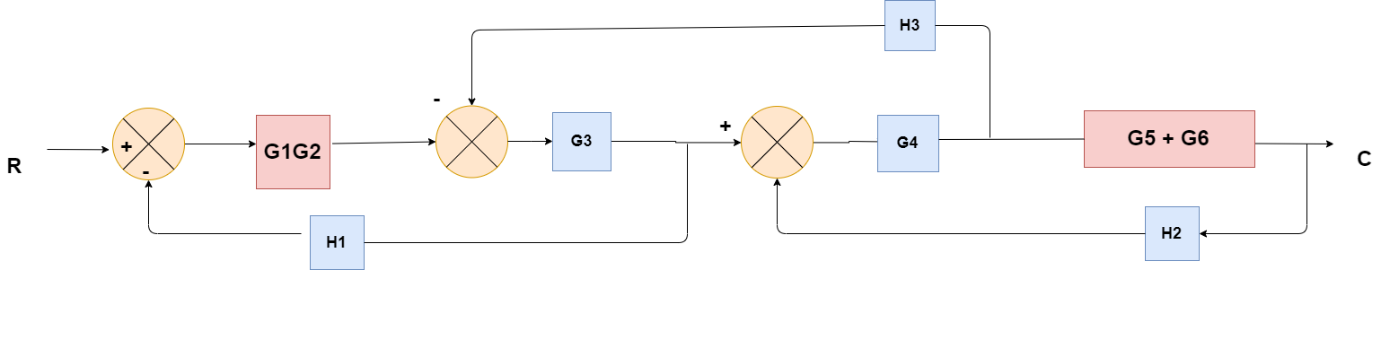
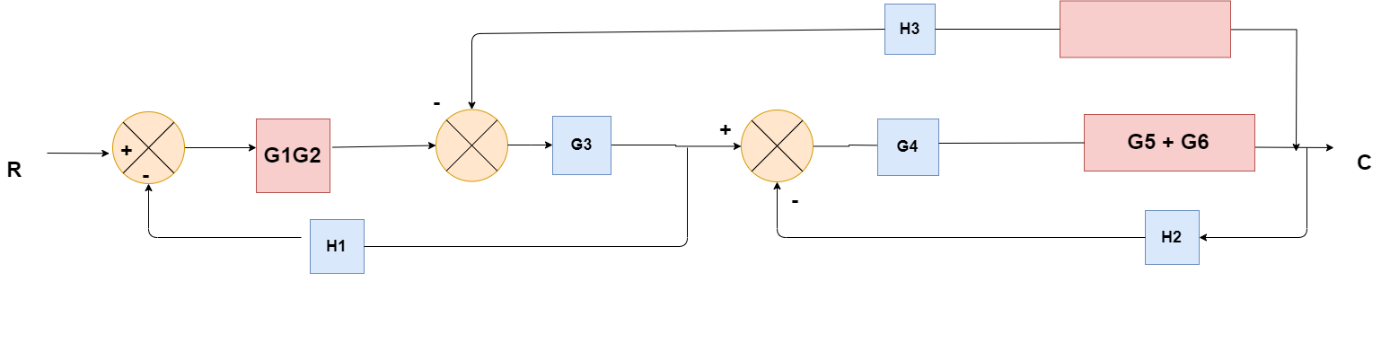
(Choose 1 answer)
(Choose 1 answer)
(Choose 1 answer)